PERIKLES (c. 490–429 BC) Ancient Greek politician, strategist...


The arrangement of the garden in the country involves the cultivation of numerous vegetables, fresh herbs, berry crops. Optimal use of its area is a skill that not everyone has. For example, planting peas will not only diversify the assortment, but also, due to their biological characteristics, peas will not take up much space. Therefore, do not deny yourself the opportunity to grow familiar green pods. By fulfilling all the requirements for agricultural technology, you will get a wonderful vegetable plant, from which you can cook a lot of tasty and healthy dishes.
The timing of sowing peas in open ground in the southern regions, in the Kuban, differs from planting in the Urals, Siberia, in the middle lane, the Leningrad Region, the Moscow Region, since the climatic conditions are different, which means the time will be different. To decide when to plant peas in the ground, you need to take into account that the seeds germinate at a temperature of + 2 ° ... + 5 ° С, they are not afraid of small frosts (up to -5 ° С).
Agronomists recommend sowing the crop as early as possible so that the beans are less affected by pests and diseases. In the spring, as soon as the soil thaws, warms up a little to a suitable temperature, start sowing. You should not wait for full warming, peas love moisture, the soil is moist after winter, which is necessary for good germination.
Now many gardeners and lovers of agriculture practice winter sowing peas, in this case, are planted on frozen soil with dry seeds when there is no more heat. When planting in winter, the seeds are not treated with anything so that they do not germinate, otherwise they will die.
For harvesting at different times, it is necessary to sow at intervals of 10-12 days. Obtaining early beans is achieved by growing seedlings at home, followed by planting in the ground. To decide when to plant peas for seedlings, you need to know the varietal characteristics and the desired harvest time.
If you want to eat green peas already in June, you should sow seedlings in March and choose smooth-grained or early (ultra-early) wrinkled varieties. To obtain pea beans in August, crops are produced in open ground in April and May. Summer sowing is usually completed before mid-July to harvest in September-October, provided that ultra-early varieties are sown.
The most common varieties of sugar peas are:
The most common varieties of shelled peas:
The time when you plant peas in open ground with seeds also depends on which variety you prefer. Every year, dozens of new varieties appear on the market, including zoned ones. For Siberia, as a rule, mid-ripening varieties are used, such as Sugar brain, May 13, Henry.
 Peas are easy to enjoy all summer long because they can be planted several times. Planting varieties is carried out in the last days of April, as soon as the sun warms up and the soil leaves after the winter cold. The next time to sow peas is recommended at the end of June. Then the fruits will fully ripen in mid-August.
Peas are easy to enjoy all summer long because they can be planted several times. Planting varieties is carried out in the last days of April, as soon as the sun warms up and the soil leaves after the winter cold. The next time to sow peas is recommended at the end of June. Then the fruits will fully ripen in mid-August.
Growing peas in open field requires the fulfillment of certain conditions: a site for peas is chosen sunny, with deep groundwater, since the roots of the plant go a meter deep and may be affected by water. The soil for peas is preferably light, but fertile, the pH of the soil should be in the range of 6-7 units: in acidic soil, the plant will be sick and weak. Peas do not like poor soils, as well as those in which there is an excess of readily available nitrogen. Some gardeners recommend sowing peas in trunk circles young apple trees, since their crowns that are just beginning to develop do not cover the peas from the sun, at the same time, the peas enrich the soil for the trees with nitrogen. If you decide on such an experiment, pour fertile soil into the near-stem circles of apple trees with a layer of 10-12 cm in height.
Despite the fact that the cultivation of peas from seeds starts in early spring, it is better to prepare the soil for peas in the fall: dig it up, adding an additional 20-30 g of potassium salt and 50-60 g of superphosphate for each m². Acidic soil is neutralized with wood ash at the rate of 200-400 g per m², depending on the value of the acid index. The following spring, before planting, 10 g of saltpeter per m² is added to the soil. Never use fresh manure as a fertilizer for peas - the plant does not tolerate it, but grows well on soils that were manured under its predecessors.
Under peas allocate areas that are clean from weeds, of medium fertility, not waterlogged, with a neutral or close to it, preferably a slightly alkaline reaction. In terms of mechanical composition, the best are medium or light loamy soils with a high content of humus, moisture-intensive and breathable soils. Heavy clay, sandy and especially sandy soils are unsuitable for peas.
The best predecessors are those crops that leave soil free from weeds, breathable, rich in nutrients and beneficial microflora: root crops, cucumber, tomato, cabbage, potatoes.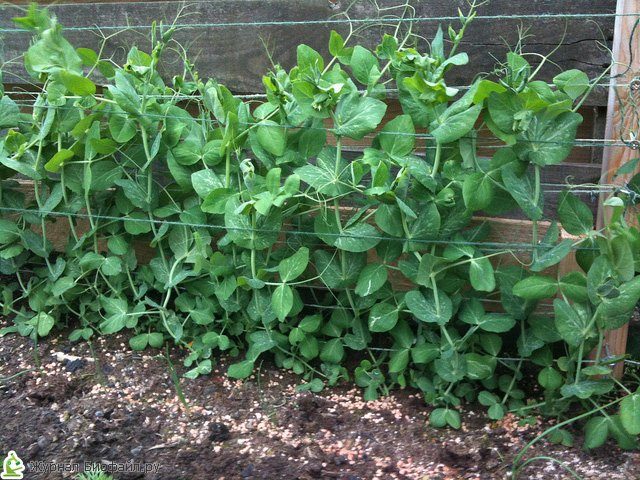 
Before sowing, the soil in the garden must be leveled and watered. The scheme for planting peas is simple. It is necessary to make shallow grooves at a distance of 50 cm from each other. Mix wood ash and compost in a ratio of 1: 1, scatter them in a thin layer along the grooves. Sprinkle fertilizer on top with moist earth from the garden and spread the seeds at 6 cm intervals. Sprinkle with soil and lightly tamp.
To protect crops from the invasion of birds, you can cover the bed from above with a special net. When sprouts emerge from the ground, it must be removed. Usually shoots appear a week after planting. 
Now you have to care for peas. It must be taken very seriously if you want a healthy, bountiful harvest.
Green peas are a common crop in Ukraine, for which 200.18 thousand hectares were allocated in Ukraine in 2016. This is quite enough to meet the needs of domestic processing enterprises and citizens.
Modern technology of agroponics allows you to get high yields and product quality.
The article will be of interest to experienced gardeners, and for novice beginners, revealing the most important aspects of growing in the country, field or. After studying our advice, you will be able to get the desired crop, and perhaps this crop will become the direction of your business, since the demand for it is quite stable.
Vegetable peas are an annual plant, pollinated independently, the flowers are white, appear 40 days after sunrise, then a fruit is formed - a bean. Beans are short, medium long, and very long, depending on the species.
The purpose of cultivation is to obtain green peas and beans. Green peas are an energy and dietary product widely used in cooking.
The first thing you need to know is that all varieties of this legume differ in terms of ripening, which will provide you with more than one collection for 2-3 months.
In addition, peas are divided by variety into:
After choosing the seed, we proceed to the preparation of the land.
Remember, there is one simple and reliable method for sorting seeds before planting. We take 1 liter of water, dissolve in it 1 tbsp. l of salt, we add to this liquid the selected ones that have surfaced - they are not suitable for landing, but those that are at the bottom - we wash and dry, here is our seed.

For the purpose of greater germination, the selected material should be soaked. Pour the selected material with warm water and wait for it to swell, changing the liquid every 3-4 hours.
You can also prepare a mixture - water and growth stimulants, in this case, soak for 3 hours. In general, the soaking process lasts no more than 17 hours, after which we plant the finished ones. This is the first method. If suddenly, you have not soaked the seeds, we plant them in the ground dry, where they will swell, but you must be prepared for the fact that the sprouts will come out a little later, but stronger.
One of the important points when disembarking is the choice of site and its quality. Sandy, acidic and salty lands are strictly contraindicated. The choice of territory is of decisive importance in cultivation technology.
The area where cultivation is planned should be globally prepared. First of all, it is necessary to level the site, since unevenness, the presence of furrows and lumps will greatly complicate the cleaning process. In addition, the area must be cleared of weeds, especially dicotyledons and perennials.
It is undesirable to sow in low relief areas that are prone to swimming (may be flooded). There is no threat if pumpkins were planted before the plants and vice versa, the soil after legumes, peanuts, lentils and peas will be unfavorable. Cereals are considered especially positive. The soil on which peas grew is useful for many crops, the yield of winter wheat increases.

For planting, we choose a sunny area, closed from the drafts of the site.
Peas are a crop that is not particularly afraid of the cold, so we sow in the last ten days of April, as soon as the ground dries out after snow. Varieties that ripen quickly can be planted until mid-July.
It is advisable to plant from late April to early July every 11 days. However, planting before the end of May is considered optimal, since full daylight hours will ensure the formation of flowers and fruits of the crop.
The area should be sunny, the soil should be light, it is desirable to prepare it in the autumn, dig up the soil, adding 30 g of potassium chloride and 10 g of urea per m². Upon the arrival of spring, apply 10 g of urea per m² to the ground. Because the trunks will grow with giant branches and low yields.
landing technology. Legumes are sown in prepared, which is dug up and loosened, in pits 6 cm deep, 15 cm wide. The distance between the pits is at least 0.5 m. Per 1 sq. meter enough sowing 60 - 100 seeds.
In order to protect against birds and insects, the territory can be covered with a net or translucent material. Long-awaited sunrises can be expected in a week. Other lettuce plants can be planted between seedlings.
The basis of care is abundant watering with loosening and weeding of the territory. A few weeks after sowing and the appearance of sprouts, it is necessary to carry out the first hilling. For sprouts over 22 cm tall, create a support in the form of stakes, between which stretch ropes or netting, which will allow the stems to curl, and not tangle and break. To get a full-fledged harvest, pinch the top shoot of the bush, and the trunk will let out lateral processes, which can also be pinned later. This procedure must be carried out at dawn.

Watering. The plant does not tolerate heat and drought, therefore, in such weather, it needs increased watering during the flowering period, it also needs abundant watering, it is poured several times a week, then weeding and loosening. Water for irrigation should not be icy, not hard in density, flowing.
It is advisable for a deeper one to install an irrigation system that turns on in the evening and works throughout the night.
Such watering will not harm the plant, will not wash away its root system, will gradually penetrate the soil and saturate it with moisture. Externally, the stems will also absorb moisture. In the morning, the irrigation system is turned off, so the plant dries out and does not get sunburned.
Fertilizer and top dressing. You can combine watering with top dressing with dry mullein, compost, humus and potassium-phosphorus fertilizers. This procedure is carried out twice, before the formation of buds and after flowering, autumn can also fertilize the soil.
Pests and diseases. Pea codling moth has always been the most harmful disease of the legume.
Butterfly, which at the time of flowering lays eggs on the plant, as a result, small caterpillars appetizingly eat all areas. In the fight against this pest, you can use chemistry - cyhalothrin. It should be remembered that this drug is used only before the formation of fruits, since it will later penetrate into food.
Going down the path folk remedies, use dandelion or onion leaves, as well as garlic.
Pour these ingredients in an amount of 2.5 kg with 10 liters of water, leave for a day and spray the plants. This tool also helps in the fight against pea aphids.
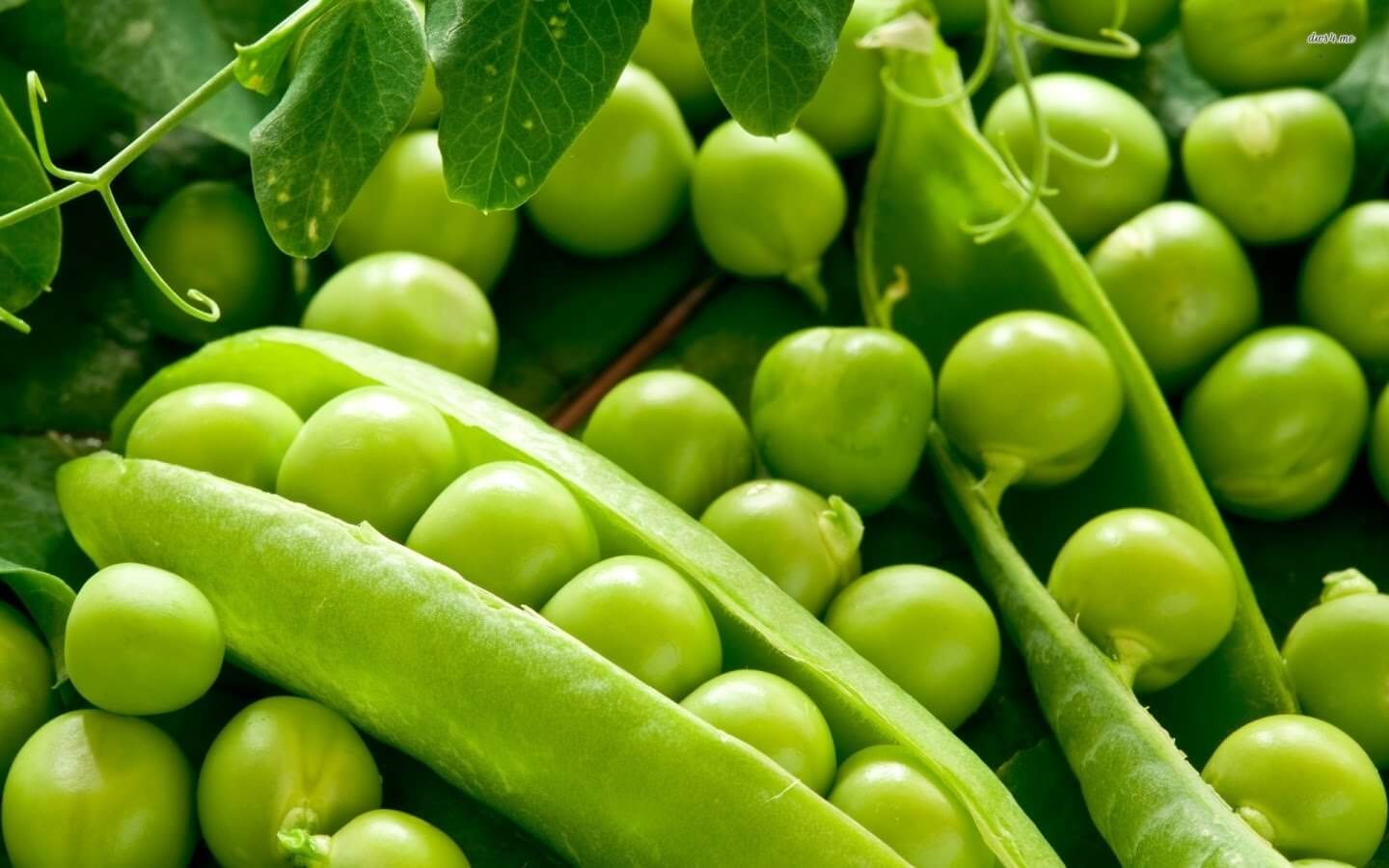

Remember that collecting pods promotes the development and maturation of new ones. Therefore, the harvest is provided to you in a day.
The pea crop is harvested, it is customary to harvest it when the peas reach their maximum size, the pod itself acquires a bright color, but before the formation of a grid on it. When a grid appears, the fruits become inedible - hard.
If you have sugar beans, pick them when the pod is flat.
Depending on the variety and purpose, the harvested crop can be used in the following areas:
If you plan to get full-fledged ones, you need lower pods, which are obtained by cutting off the trunk at the very root and placing it in a closed, dry and unventilated area.
Seeds remain viable for more than two years.
The tops can be used as compost, which is added to the soil.
While watching the video, you will learn about growing peas.
Well, here we have presented the main secrets of growing peas in the open field, using which success in this interesting and useful process is ensured!
Noticed an error? Select it and click Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
There is no doubt about the benefits of green peas. However, not everyone knows how to provide their table with this useful culture from spring to frost. There are several factors to consider when growing peas, including planting dates and cultivars.
This crop is not planted with seedlings, so you need to correctly determine the timing of planting peas. First of all, you need to focus on the varieties, since they differ in the timing of the ripening of the pods.
Sowing of peas in the ground in terms of time is carried out in two versions: from April to May and from June to the first decade of July. About everything in more detail.
Since spring comes to each region at different times, plantings should be guided by soil temperature. When the earth warms up to + 2-3 ° C, these are optimal conditions for pea sprouts. Even if there are return frosts, shoots will be able to transfer them. However, the root system of peas develops only in warm soil and with sufficient moisture. Pea seeds begin to germinate at a temperature of +2-3°C.
The early dates for planting peas are related to the fact that there is enough moisture in the soil or you will have to water the ridge daily. It should be borne in mind that pea seedlings appear on the 7-10th day and throughout this time it is necessary to provide the soil with a sufficient amount of moisture.
If you look at the landing date, then they are held around the third decade of April. After sowing the seeds, the ridge is covered with any covering material to retain moisture and prevent birds from pecking at the seeds.
Many summer residents determine the timing of planting peas according to lunar calendar. In any case, sowing is carried out on the growing moon, when the seeds have more strength for active growth.
Peas do not tolerate heat and high temperatures, therefore, from May to the end of June, even with timely watering, such seedlings will not give a good harvest. It is much easier to sow late-ripening pea varieties in the spring to get fresh pods throughout the summer.
In July, the area is freed from garlic and the question arises of what to plant in this place. If the weather is right (no extreme heat and fairly humid), peas can be sown. Depending on the variety, green pods are harvested from August to September. Agrotechnics of cultivation during this period does not differ from spring. The only thing is, if the heat returns, you will have to lightly shade the pea crops with any light material, for example, spandbond, and water more often.
Previously, the day of sowing peas was also determined by the state of the moon, but there were other signs.
Have a good harvest of peas!
Peas are an annual legume plant. Fresh, it is a very tasty delicacy, sweet in taste, loved by both children and adults. It will be tasty only until that moment until the sugar peas in the pod become coarse.
Want to know more? Subscribe to our VK public, there is all the most delicious from the editors and interestingness from readers:
In contact with
In dried form, peas are used to make soups and cereals, which are quite nutritious. Green canned peas- one of those vegetables that is necessarily present on any holiday table in salads and other dishes.
Peas are ahead of all other vegetables in their protein content. It also contains starch, sugar, fat, amino acids, vitamins A, C, B1, B2, minerals - phosphorus, potassium, magnesium.
Dishes from peas are recommended for anemia, constipation. A decoction of grass and pea seeds is used as a diuretic for kidney stones. Pea flour is used to soften the abscess. Peas help improve brain function, reduce blood sugar when diabetes, improve metabolism.
The great importance of peas lies in the fact that it is used as a fodder crop for livestock. Crushed and steamed pea chaff is given to cattle. To improve the weight gain of animals, as well as to improve the quality of meat, animals are given concentrated feed from pea flour.
Peas are able to enrich the soil with nitrogen compounds. The tubers of the culture, formed on the roots of the plant, contain microorganisms that absorb the nitrogen necessary for the plant from the air.
At the same time, they receive mineral salts and water from them. Thanks to this valuable property, peas easily grow on depleted soils. And after its death, the plant leaves the soil enriched with nitrogen.
Thus, the soil does not require additional application of manure to it. For other crops, peas are an excellent predecessor.
Sugar - in turn, they distinguish dessert and shoulder varieties.
 Dessert pea varieties are distinguished by sweet and tender beans that can be consumed both fresh and boiled. Spatula varieties are used for making soups and side dishes.
Dessert pea varieties are distinguished by sweet and tender beans that can be consumed both fresh and boiled. Spatula varieties are used for making soups and side dishes.
Shelling. Beans of this variety have a thick parchment layer on the inside. The seeds of shelling pea varieties are mainly eaten. Beans that are green and unbleached can be consumed fresh. Shelling varieties of peas are dried and used to make soups and cereals.
Before you start growing peas, you should decide on the choice of crop variety, allocate for it a plot of land well-lit by the sun.
Planting peas is carried out at the earliest possible time, when the soil is most saturated with moisture after winter. This is due to the fact that the plant is moisture-loving. Later on April 22-25, planting peas is not recommended. The culture is resistant to low temperatures; pea seeds can also germinate at an air temperature of +1 ... + 2 degrees; young shoots withstand frosts down to minus eight degrees.
First, the pea seeds must be warmed up, then sorted and separated from diseased and non-standard crop seeds. For 5 minutes, lower the seeds into a hot solution of micronutrient fertilizers containing ammonium molybdate and boric acid(2 g of fertilizer per 10 liters of water). This treatment helps to reduce seed damage by the nodule weevil larvae.
 Both dry and swollen pea seeds are planted. In order for the peas to germinate faster, they are soaked overnight. Seeds that have been soaked in water can deteriorate and should not be planted in soil. It is good to treat the seeds with nitragin and rhizotorfin before planting at the rate of 0.5-1.6 grams of fertilizer per 1 kg of seeds.
Both dry and swollen pea seeds are planted. In order for the peas to germinate faster, they are soaked overnight. Seeds that have been soaked in water can deteriorate and should not be planted in soil. It is good to treat the seeds with nitragin and rhizotorfin before planting at the rate of 0.5-1.6 grams of fertilizer per 1 kg of seeds.
Early sowing of peas is covered with a film, since on cold soil damage to seeds by soil pests is possible. You can plant crops and monthly seedlings. The second decade of May is a great time for planting seedlings in a permanent place. Plant transplantation is relatively well tolerated.
A furrow is made along the beds with a width of 16-25 cm. The distance between the furrows is 50-70 cm. The furrow is filled with compost or humus, ash and complex fertilizer are added, soil is applied on top and well leveled. The depth of the furrow after all this should be no more than 3-5 cm. It is best to do all this in advance.
 At a distance of 5-8 cm from each other, peas are scattered over the entire area of the furrow. After that, they are sprinkled with earth from the sides in such a way that the peas remain at a depth of no more than 5 cm. The soil is well compacted with the back of the rake. This is necessary in order for moisture to flow normally to the seeds of the plant.
At a distance of 5-8 cm from each other, peas are scattered over the entire area of the furrow. After that, they are sprinkled with earth from the sides in such a way that the peas remain at a depth of no more than 5 cm. The soil is well compacted with the back of the rake. This is necessary in order for moisture to flow normally to the seeds of the plant.
Small bumps along the edges of the groove are best left. Pegs are inserted in the center of the groove at a distance of 1-1.5 m, on which a high metal mesh with large cells is fixed. It serves as a support for the plant. On the 7-10th day after planting shoots appear.
You can plant peas with three-line ribbons: the distance between the lines should be 10-15 cm, and between the extreme rows - 6-10 cm, the depth of the lines - 3-5 cm.
Peas must be protected from birds. To do this, the seedlings are covered with a net or threads are pulled. In the initial period of growth, the soil around the plant must be loosened and hilled. Thus, there is protection from the pea weevil, which eats the edges of the leaves. Water the plant in dry weather, feed once every one to two weeks. The first feeding is carried out when the plant reaches a height of about 8 cm.
During flowering and pouring beans, watering and top dressing are especially needed. Irrigation rate: 8-10 liters of water per 1 sq. meter of planting area. Together with watering, they combine top dressing of the plant. Top dressing is also necessary when the plant is oppressed. Top dressing: 1 tablespoon of nitroammophoska per 10 liters of water, consumption rate: 10 liters per 1 sq. m of landing area. When using a solution of mullein, the amount mineral fertilizers reduce.
 To increase the yield, harvesting of ripe beans should be carried out constantly - every 2-3 days. It is also necessary to remove overripe beans, as left in this state on the plant, they stop the growth of new beans. When tearing off the pod, it is necessary to hold the stem of the plant with one hand. Peas bear fruit within 4-6 weeks.
To increase the yield, harvesting of ripe beans should be carried out constantly - every 2-3 days. It is also necessary to remove overripe beans, as left in this state on the plant, they stop the growth of new beans. When tearing off the pod, it is necessary to hold the stem of the plant with one hand. Peas bear fruit within 4-6 weeks.
To obtain grains, the beans are left on the bush for further maturation. As soon as the lower pods are fully ripe, the plant is cut at the root, tied into bunches. For final ripening, hang in a ventilated room for one to two weeks. For two years, the plant retains seed germination.
Pea codling moth (leaflet)- the most malicious enemy of peas. The caterpillars of this pest remain to winter in the soil, and during the flowering of peas, butterflies fly out of the cocoon. Each butterfly is capable of laying more than 200 larvae on pea flowers, leaves, stems and beans.
 For 6-10 days (depending on weather conditions), caterpillars appear from the larvae, which penetrate the beans and remain there to live, while feeding on young peas. Thus, wormholes are formed in the grains that can completely destroy the peas.
For 6-10 days (depending on weather conditions), caterpillars appear from the larvae, which penetrate the beans and remain there to live, while feeding on young peas. Thus, wormholes are formed in the grains that can completely destroy the peas.
To combat pea codling moth, the plant is sprayed with decoctions of bitter wormwood, infusion of burdock roots, decoction of tomato tops, infusion of celandine leaves, garlic and tobacco. To prepare an infusion of garlic, you need to pass 20 grams of garlic through a meat grinder, then pour it with 10 liters of water and insist for a day, then filter the infusion and spray the plant with it.
Spraying is best done in the evening. With such a solution, the plant can also be treated for preventive purposes, without waiting for the appearance of the pea codling moth. An infusion of garlic also helps in the fight against pea aphids. Dusting the plant with ash, dry celandine powder and tobacco helps in the fight against codling moth.
An effective means of protection against the codling moth is winter digging of the soil and early sowing of peas. To prevent this disease, it is recommended to warm the pea seeds immediately before planting.
powdery mildew- Another common disease of peas. To combat it, use an infusion of field sow thistle, which is prepared as follows: take 300 grams of sow thistle leaves in a bucket of water and insist them in water for 8 hours. Plants are sprayed at intervals of a week.
Very often, many gardeners simply simply do not attach much importance to planting peas on the site. But this is not true. After all, it is a valuable, vitamin and nutritious vegetable, versatile in use. With all this, he fertilizes the garden, and does not deplete it. He deserves to be grown!
In contact with
See inaccuracies, incomplete or incorrect information? Do you know how to make an article better?
Would you like to suggest photos for publication on a topic?
Please help us make the site better! Leave a message and your contacts in the comments - we will contact you and together we will make the publication better!
How to grow juicy peas for personal use in the country? If there is a small free bed left in the garden, plant sweet peas on its territory. This pretty herb is very popular fresh with children and will also help organize many meals for adults. Today we will talk about growing peas in the country and consider its agricultural technology.
Pea is a herbaceous legume plant. A green, curly and very pretty annual becomes at some point a supplier of a sweet and juicy product, which differs not only in its original taste, but also in the content of nutrients.

Peas are considered a finicky plant, but growing them in the country, subject to certain rules, is quite simple. Peas are sown in spring, in more or less warm soil. The root of the pea goes deep into the ground, and therefore the plant requires preliminary digging of the soil, preferably in the fall. In the same period, it is better to apply complex fertilizers.

Pea is a warm and light-loving plant, which grows well in quiet, calm and well-warmed areas. It is very important that the soil in the area for planting peas be minimally fertilized - it is enough to apply mineral fertilizers and organic matter. It would be nice to treat the soil with lime, up to 250-300 g / m2, and also add 30 g of potassium and 20 g of double superphosphate.
Be prepared for the fact that you will have to correctly navigate the laying of seeds when sowing. In heavy and clay soils, peas are grown almost on the surface; in lighter soils, planting occurs deeper.

Prepare in advance to install supports for adult peas, since the plant cannot simply be left on the ground, in this form it will not give the desired result.
Before planting, the seeds should be carefully sorted out, spoiled, broken. The rest need to be warmed up and soaked for 5-7 minutes in a solution of boric acid (1 g per 5 liters of water). Landing takes place in a swollen, but dried form.
You can also use growth stimulants, but is it worth it if properly prepared peas at home already give normal shoots ...
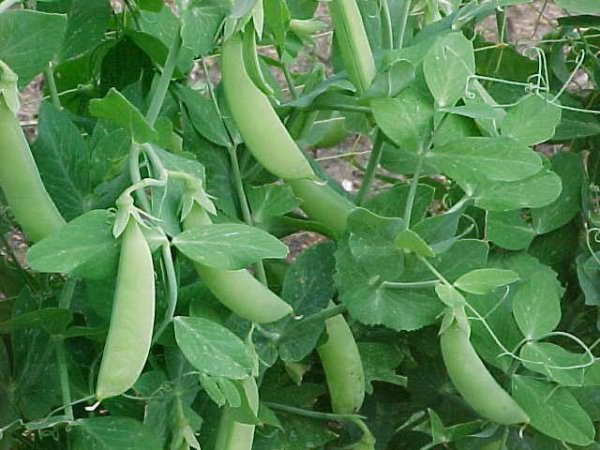

Sowing peas in the country takes place around the middle of spring, but at the moment when the soil is warm enough. Sowing goes with a certain density - undersized peas are sown thicker, taller peas are sown less often.
A bed for sowing peas is prepared very simply. First, furrows are made along the bed with a depth of 5-7 cm. The distance between them is 50-60 cm. The furrows should be prepared in advance, a few days before planting, and a mixture of compost and ash should be added to them, which is sprinkled with earth from the garden. After preparation and application, the depth of the beds for sowing peas should be 3-5 cm. But here, do not forget to focus on the composition of the soil!
Peas are sown 15-17 pieces for each meter of the bed, that is, approximately every 6 cm. The crops are sprinkled with earth and lightly compacted to preserve moisture. After one to one and a half weeks, you will be able to see the shoots of peas.
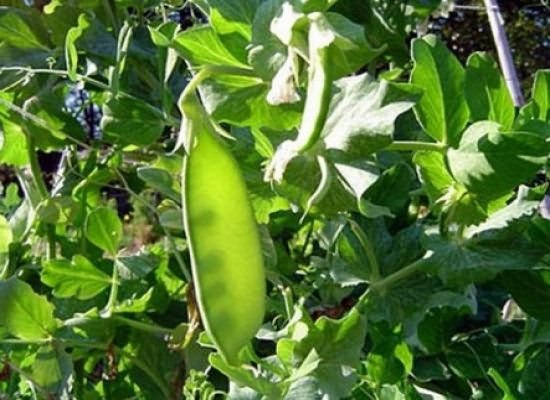
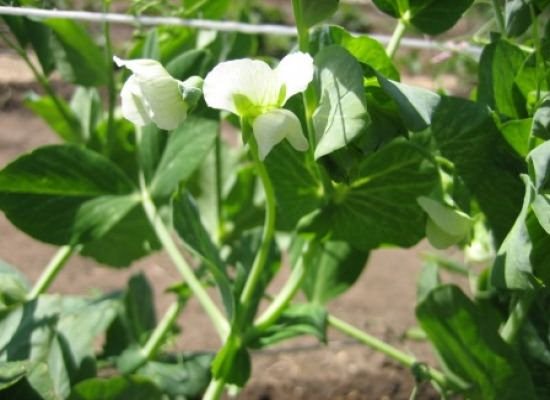


The greatest danger is the pea stalk or leaflet. After wintering in the ground, pest caterpillars turn into adult butterflies and lay their eggs on pea greens, in flowers and leaves. Caterpillars reappear from these eggs, which quickly eat young plants and seriously spoil the crop.
Powdery mildew can also become an unpleasant problem for peas, which affects the entire plant and reduces the chances of getting a crop.

Best of all, according to experts, the following varieties of peas are suitable for summer cottage cultivation of peas: Avola, Strizh, Pegas, Vikma, Geneva, Skinado, Violena, Salyut, Karina, Chinese, Ilovetsky.

Grow peas in the country with pleasure, since its fresh fruits are suitable not only for eating raw, immediately from the garden, but also for preparing so many delicious and healthy dishes. Thank you for your attention to our article and we invite you to discuss in the comments, especially if you have recommendations or tips for summer residents! We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the material on how to rid the garden of wild hops.
DachaDecor.ru
Despite the widespread and popularity peas in summer cottages, not everyone can get a good harvest of this crop, since it has its own secrets of growing.
All varieties of peas are divided into four varieties: fodder, grain, vegetable (shelling) and sugar. Gardeners use the first two varieties to obtain organic fertilizer and sow them after
digging potatoes or harvesting cucumbers, early cabbage, radish, lettuce. Green peas bark only peeling varieties. They have beans with a parchment layer, which makes it easy to thresh peas. Sugar
varieties are planted for the use of young beans in writing as a whole. In grain varieties, green peas are of poor quality and contain few sugars. But ripe seeds are easily boiled, so they are harvested for soups.
The technology of growing peas should maximize the formation of flowers and their pollination in order to ensure a good harvest. To do this, one should take into account its relationship to four environmental factors - heat, light, humidity and batteries.
Peas belong to the group of the most cold-resistant plants. Seedlings appear at a temperature of +4-5 ° C. They are not afraid of short-term frosts, but at high temperatures (more than +20 ° C) the plants grow slowly and form small beans with a small amount of green peas. The optimum temperature during the growing season ranges from +20 °C.
Peas are very picky about light. When shading, it grows poorly - it stretches, the stems lie down and break, and the yield decreases. Tall varieties are especially sensitive to shading, so they are planted sparsely. Some varieties react to the length of daylight hours and do not bloom in autumn when sown in summer to obtain a crop.
and air. The largest quantity Peas require moisture two weeks before mass flowering and fruiting. Its deficiency leads to the rapid conversion of sugars into starch, which is undesirable for high quality green peas and sugar tender beans. However, peas do not tolerate waterlogging of the soil. For example, in swampy suburban areas, plants quickly turn yellow and die, and if it is still cold, there is a risk of infection of peas with root rot.
The short vegetation period of the crop requires a high level of soil supply with nutrients. The special value of peas is that nodule bacteria develop on its roots. They fix atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into amino acids and protein. After the plants die, nitrogen enriches the soil. This culture grows well only on neutral and slightly acidic soils with a lot of calcium. Acidic marshy and alkaline saline soils are not suitable for him.
Peas may not be combined with all vegetable plants. To create natural supports on a pea bed, cold-resistant vegetable beans, ornamental sunflowers or oats are sown. It is better to choose a well-lit area where any
vegetable and ornamental plants, except legumes. After peas, you can sow or plant any crops that still have time to form a crop before the end of autumn - black radish, white and daikon, Peking and cauliflower), kohlrabi, sweet corn and asparagus beans, lettuce, spinach.
Peas are self-pollinating vegetable plants, which makes it possible to sow different varieties nearby. If you choose them correctly, this culture will bear fruit continuously. It is best to simultaneously sow 4-5 varieties with different growing seasons at the optimum time. Or sow one early-ripening variety every 7-10 days. But in the second option late dates yield will be unstable.
Peas are sown in early spring, therefore) soil preparation begins in the fall. The soil is dug up, humus and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied (50-60 g of superphosphate and 20-30 g of potassium salt per 1 m2). Acidic soils are fed with wood ash. In the spring, the plot for sowing is fertilized with a small amount of saltpeter (up to 10 g / m2). sufficient for intensive initial growth. Seedlings of peas will be rare or will not sprout at all if the beds are dug up only in the spring, as this will lead to the drying of the topsoil.
The timing of spring sowing coincides with the period of the first field work. First, the bed is leveled with a rake, nitrogen and other fertilizers are applied, and marked in rows. Then grooves are made with a hoe to a depth of 5-6 cm and peas are sown. After planting the seeds, the rows are lightly rolled with a roller or pressed down with a foot.
If the bed is narrow, not wider than 1.5 m, then sowing grooves are made every 15 cm. If it is wide, then for the convenience of caring for the plant and harvesting) when giving birth, peas are sown in ribbons of 2-5 rows. 45-50 cm are left between the ribbons. 110-120 seeds of low-growing early-ripening varieties and 90-100 late-ripening ones are sown per 1 m2. Tychkovy tall peas are sown in two rows of ribbons, leaving 20 cm between them, and 60 cm between the ribbons. 50-60 seeds are sown per 1 m2. The free space between the ribbons in the spring can be sown with lettuce, spinach, radish, or planted shallots. These plants will free up this space in a month and a half.
After the seedlings have appeared, weeding and loosening of row spacings are regularly carried out until the peas begin to bloom. With a plant height of 12-15 cm, they can be lightly hilled with a short break. This technique is used mainly in small areas. When hilling, seedlings of weeds fall asleep, so the peas acquire greater stability. Bonded varieties are especially responsive to hilling. In dry weather, it is advisable to water the peas several times. If you need to speed up fruiting, on a small part of the plot, you can pinch the tops of the stems after the third or fourth inflorescence.
Harvest every 2-3 days. For shelled peas, the beans should be fully fleshed out, but still juicy and green. The size of green peas reaches 6-7 mm. During this period, it is of the highest quality. In sugar varieties, beans are removed at the first designation of the seed site. Then the parchment LAYER Inside the sash and fiber along the bean seam are undeveloped and the quality is the highest. Green peas are eaten raw, frozen, dried for the winter.
Peas are often attacked by weevils, scoops, nematodes, tripe. But since this is a dietary product, it is better to use safe methods fight. For example, the rotation of vegetable plants is effective against nematodes. In dry
and hot years, only aphids cause tangible harm to peas. At the first sign of a plant colonization by this pest, it is worth scaring it away with decoctions and infusions of wormwood, garlic, onion peel, fragrant onion leaves, tansy and tobacco dust. For better adhesion, add a little soap or boil soapwort roots. Increases resistance against aphids and the introduction of potash fertilizers in the fall. The harmfulness of the pea grain beetle (bruchus) does not matter for obtaining green peas. Damage by other pests is not so significant.
According to the duration of the growing season from germination to technical maturity, all varieties are divided into ultra-early, early, mid-early and mid-ripening. Early maturity is closely related to plant height - the higher it is, the later and less productive the variety. Also, this characteristic affects the quality of green peas. In early ripening varieties, sugar is converted to starch faster, which requires intensive harvesting. To obtain green peas in autumn, early ripening varieties are used, which are sown in July. Sugar varieties of peas are more tender, more demanding on the implementation of the recommended technological methods and less productive than other varieties.
In dachas, late-ripening "poke" ("stake") varieties of peas with a height of more than 1.5-2 m are sometimes grown. Such plants require supports and the periodic direction of deviated shoots. Supports are placed after the formation of 3-4 leaves. Bonded varieties can also be used for landscaping the site.
Early maturing varieties of peas are planted in the middle of summer - to obtain green peas.
Sugar varieties are more demanding on growing technology and less productive.
This variety is used for food consumption and as a decoration for landscaping.
The short growing season of peas requires a full supply of nutrients.
To accelerate the fruiting of this crop, pinch the tops of the stems.
Peas early term crops are less damaged by the pea codling moth. Caterpillars are dangerous because they eat away the seeds inside the green pods.
Good and productive varieties of peas
1. AMBROSIA
Polish variety of early maturing terms. The beans are juicy and tasty, up to 8 cm long, with 6-7 sweet seeds. Young beans can be used as a sugar variety. Plant height up to 70 cm. An early maturing variety, you can get an additional crop with late summer sowing.
2. SKINADO
Dutch variety of medium-early ripening.
You can get early production with early sowing in the spring. Plant height up to 80 cm. The length of the bean is 7-8 cm, the number of seeds is up to 8 pcs. One of the best varieties for freezing. The variety is resistant to root rot and yellowing of the tops of the stem.
Z.WADA
Dutch grade of average terms of maturing. It is suitable for cultivation at all terms of crops. Plant height 70-80 cm. Bean length 9-10 cm, forms up to 10 seeds. Differs in intensive formation of beans which are formed on a top of plants, very highly productive. Excellent variety for green peas.
4. GENEVA
Dutch grade of average terms of maturing. Suitable for growing at spring sowing dates. Plant height 85-95 cm. Beans 9-10 cm long form 9-10 small seeds. The variety has a high yield.
5.DINGA
German variety of medium ripening. In warm years, it ripens at the level of early ripening varieties. Plant height up to 85 cm. Bean is large, up to 10-11 cm long, with 7-9 dark peas. Ripe seeds are wrinkled. Excellent for green peas at spring sowing dates. Highly resistant to Fusarium.
6. AVOLA
Early maturing variety. Plant length - 67 cm, forms up to 12 beans. The variety is adapted for growing green peas, canning and fresh use. Zoned in all climatic zones of Ukraine.
7. Swift
New grade of the Ukrainian selection, average term of maturing. The length of the stem is 85-92 cm. The number of seeds in a bean is up to 9 pcs. The variety is used for fresh consumption, drying and canning.
8. VIKMA
Mid-season variety of Ukrainian selection. Stem length 85-100 cm. Pods 8-10 cm long, form 9-10 brain seeds. Recommended for fresh use and for canning.
9 Pegasus
High-yielding mid-season variety. Stem length 80-90 cm. Beans 8 cm long form 7-8 medium-sized brain seeds. The variety is adapted for growing green peas, canning and fresh use. Zoned in all climatic zones of Ukraine.
10. MOSCOW DELICATE (DELICIOUS)
Russian variety of medium ripening. In cool years - medium-late. Plant height up to 80 cm. Beans 6-8 cm long, peas are large and sweet. It is recommended for cultivation at early-spring terms of crops.
11. PURPLE
A new Russian variety of medium ripening. Plant height 70-80 cm. Purple beans, up to 8 cm long. The variety is decorative, used in landscape gardening. So far, little studied in terms of yield and disease resistance.
12. KARINA
Dutch universal variety of early ripening. Stem length about 73 cm. Beans with an average number of seed primordia, medium length, narrow, yellow in color, with pronounced parchment. The variety is used for canning and fresh.
13. VIOLEN
Early variety. Plant height 60-66 cm. Pods 7.5-8 cm long, they contain 7-8 brain seeds. The variety is adapted for growing green peas, canning and fresh use. Zoned in all climatic zones of Ukraine.
14. SALUTE
Early variety. The plant is 58-82 cm long. The beans are 8-9 cm long, 7-9 brain seeds ripen in them. The variety is adapted for growing green peas, canning and fresh use.
15. ILOVETSKY
Russian variety of medium-early ripening. The plant is up to 55 cm high. Beans are 4-5 cm long. Young sweet beans are used for food when green peas are still small and do not exceed 3-5 mm. It grinds badly. It is recommended for cultivation at all terms of crops.
16. CHINESE
Chinese collection variety. Mid-season. The plant is up to 70 cm high. The beans are large, 12-14 cm long. Only young sweet beans are used when the green peas are still small and do not exceed 5 mm. It grinds badly. It is recommended for cultivation at spring terms of crops. Great for freezing whole beans.
Pea Dishes
When it comes to what can be cooked from peas, for some reason, only the banal pea soup comes to mind. But green peas can be combined with many products, getting original, and most importantly - delicious dishes.
GREEN PEA CREAM SOUP
INGREDIENTS:
1 large onion
4 strips of bacon or smoked bacon
2 medium potatoes
400 g frozen green peas (fresh peas in pods must be very young)
800 ml chicken broth
salt, black ground pepper
1 a. l. vegetable oil
COOKING STAGES
1. Cut the onion and bacon into cubes.
2. Fry bacon and onion in vegetable oil until golden brown.
3. Peel and cut the potatoes into pieces, boil in chicken broth, add defrosted peas and sauté. Cook over high heat for 5-7 minutes.
4. Grind the soup with a blender, add salt and pepper to taste. The blender must be used with a metal nozzle. Before serving, decorate the dish with the rest of the onion sauté and herbs. Can be served with wheat bread.
LECHHO IN BULGARIAN
FOR 4 SERVINGS COOKING: 30 MIN.
INGREDIENTS:
1 chicken thigh, boned
4 medium potatoes
2 large onions
4 small bell peppers
4 tomatoes
salt pepper
vegetable oil
COOKING STAGES
1. Cut the chicken and fry until half cooked and golden brown.
2. Peel the potatoes, cut into small pieces and add to the chicken. Fry until potatoes are half cooked.
3. Add chopped onion and pepper to the resulting fry
and fry for another 5-7 minutes. (you can add water or chicken broth). A. Add chopped tomatoes and peas, close the lid and simmer for another 10 minutes. Before serving, the dish can be sprinkled with chopped dill or parsley.
SNACK "VEGETABLE TRIO"
INGREDIENTS:
1 large carrot
1 small onion
2 pieces of bacon or smoked bacon
200 g thick mashed potatoes
1 cup green ice cream peas
ground black pepper and salt
vegetable oil
a few sprigs of fresh basil
COOKING STAGES
1. Peel the carrots and boil them whole until tender. Cut into slices and sauté in vegetable oil with finely chopped half of the onion. Add pepper and salt.
2. Grind carrots with onions in a blender until a homogeneous puree is obtained.
3. Cook peas for 10 minutes. Drain the water, and then sauté in vegetable oil with smoked lard and half an onion. chop peas
in a blender, after adding a few sprigs of fresh basil.
4. Put all three purees in layers in cups, pour cheese sauce on top. Serve the appetizer warm.
Peas peas strife!
Therefore, when buying its seeds, I pay attention not only to the beautiful packaging, but also to the words written on it. Which is what I advise you.
There are three types of peas: brain, shelling and sugar.
sugar peas good in salads, it can be canned. Young pods are eaten whole! Well, there is nothing to say about the taste, the name sugar speaks for itself. But I do not recommend drying it for the winter.
The most popular - shelling peas. Having planted it, you can eat delicious pods, and prepare them for the future. After all, it is he who is dried for the winter for soups and cereals. And at the beginning of fruiting, shelling peas are in no way inferior to sugar in taste. But it is worth it to overexpose a little on the bush, as it becomes tough and acquires a floury flavor.
And another view - brain pea.
His peas are sweet, almost the same as those of sugar peas. It is suitable for canning, but it is better not to cook soup from it - the peas are very soft, and you will get not soup, but mashed potatoes.
I never feed my peas, as spring humus dressing is enough for them.
I usually plant only shelled and sugar peas. The first one goes for the winter - I dry it and cook different dishes. The second is for grandchildren, so that they can feast from the garden. My husband and I also love to eat sweet peas.
Where to plant peas
My pea beds are located in a well-lit and ventilated place. After all, growing up, its lashes are quite tightly intertwined and various pathogens or pests can settle inside, which will be dangerous not only for peas, but also for other plants in the garden. So blowing the landings with a breeze is a kind of prevention from all misfortunes. The land there is loose and fertile - every year I bring in humus from the compost bin.
sprouts of peas
In order for the peas to rise quickly and amicably, I definitely warm it up. The easiest way is to put the peas on the windowsill for 3-4 days. The spring sun will warm them up, and shoots will appear faster. You can also immerse the peas in hot water, but its temperature should not exceed +50 ° C, otherwise you will just boil them.
If you are using not purchased peas, but your own, harvested last year, then it must be examined for the presence of a pest - pea grains. These are small black bugs that feed on peas. If you notice such or holes in peas, then the entire batch of peas will need to be soaked in salt water (30 g of salt per 1 liter of water). Already unsuitable for sowing - those. that the grain has gnawed - will emerge. Collect them with a slotted spoon and discard. Rinse the rest well and dry.
I sow every year differently. Because the weather is so changeable. But usually no later than mid-May. Seedlings withstand slight cold snaps. I make the distance between the rows quite large - 40-50 cm, since the peas will bush and lean on each other. Yes, you also need a place to stand. But the distance in the row is only 5-8 cm. I loosen the soil, level it, make holes about 5 cm deep with a stick, and throw one pea into them. I push the same stick to the very bottom, and sprinkle with soil on top.
About feeding
I never feed my peas, humus dressing is enough. Well, I want to remind fertilizer lovers that it is generally not recommended to add nitrogen to the soil, because pea roots produce it themselves.
This is how I grow my fabulously delicious peas, which the whole family enjoys.
vsaduidoma.com
Why grow peas?This is due to the fact that peas are an indispensable food product rich in proteins, vitamins - K, E, B1, B2, A, C, PP, carbohydrates, fiber, minerals - phosphorus, iron, potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, etc. It has a well-pronounced therapeutic effect on the human body. In addition, pea tops are excellent feed for livestock. Peas are also used in agriculture to enrich the earth with nitrogen. What varieties of peas to plant?Varieties of peas are divided into two large groups: shelling and sugar. The surest distinguishing feature of shelling pea varieties is the presence of a special parchment layer in its seeds. Such varieties of peas are good for getting green peas. Only grains are used for food. Among the peeling varieties, one can single out Korvin (40 days), Sherwood (55 days), Early-301 (45 days), Ashton (50 days), Matrona (60 days), etc. Seeds of sugar varieties do not have a parchment layer. They eat both grain and pea bean leaves in an unripe form. Such sugar varieties as Zhegalova-112 (50 days), Soup spatula-181 (45 days), Inexhaustible-195 (68 days), Cascade (55 days) and others are popular with vegetable growers. Peas in terms of ripening can be early-ripening, mid-ripening and late-ripening. Therefore, in order to get a crop all summer, you need to simultaneously sow pea varieties with different ripening dates, or your favorite variety, but with an interval of 10 days. Where is the best place to sow peas?A place for growing peas should be chosen sunny and open with fertile and loose soil. It is best if its predecessors are potatoes, pumpkin, cabbage, cucumbers. How to sow peas?Peas are not afraid of the cold, so this crop can be sown already at a soil temperature of 5-8 degrees. Its grains do not need to be soaked before sowing. First of all, before sowing, the place chosen for growing peas is dug up and watered. Then, grooves of the same depth, about 5 cm, at a distance of 20-25 cm are made with a shovel handle. It is worth counting on good germination of peas when AVA fertilizer is applied to the soil (10 g per 1 linear meter). Instead of this fertilizer, you can use a mixture for 1 linear meter: a bucket of humus, 200 g of dolomite, 400 g of ash, 10 g of superphosphate, 10 g of potassium. Peas do not need nitrogen fertilizers, because. itself is a factory for its production. Pea grains are laid out in pairs in grooves made every 10-15 cm and covered with earth. From above, the landing site should be covered with a transparent film to protect the seeds from birds and create a special microclimate for quick seed germination. Sowing time for peas is from mid-April to the end of May. How to care for peas?To get a decent harvest of peas, you must adhere to the following rules:
Pea culture loves moist soil, so the soil should not be allowed to dry out. It should, as weeds appear, weed the beds with the crop, loosen the soil. Peas well accept top dressing with potash and phosphorus fertilizers. Tall varieties of peas, when growing, should be tied to specially prepared trellises. But the gardener, in order to look decent on the way to the dacha, should think about where to buy T-shirts in order to be always on top, like a pea pod. Among the pests of peas, aphids and pea weevil are often found. Preventive measures in order to prevent the appearance of aphids are carried out as follows: treatment once every 10 days with infusion of pod hot pepper, garlic or onion. The pea weevil is well destroyed by the Fitovermite solution. To avoid plant diseases such as powdery mildew, you should spray them with Fitosporin solution once every 2 weeks. How to collect peas?To eat peas raw, they should be picked while still green, unripe, while the pods have not yet turned yellow. On the contrary, for long-term storage, you should wait until the pods turn yellow. Peas can be harvested from June to the end of August. Take it off early in the morning to keep it fresh longer. When harvesting peas, due to its weak root system, one should hold the stem with one hand, and carefully pick the fruit with the other. How to store peas?The main methods of storing peas are freezing, canning and drying. It is best to eat fresh peas. However, even at proper storage it can retain its beneficial properties for a long time. What can be cooked from peas?In many cuisines of the world, peas are used very widely. It is a part of many vegetable soups, festive salads, porridge is cooked from it, pancakes are baked, a side dish for meat is made, stuffing for pies. Thus, by correctly observing the cultivation technology, you can get a rich harvest of peas and provide yourself and your loved ones with a very valuable product for the whole year! List of references on the topic:1. Vasilchenkova V.V. Pea cultivation technology.// Agriculture, 2002; 2. Letunovsky V.I., Sinitsin E.M. Guide to growing peas//M: Agropromizdat, 1996; 3. Kuleshova I.M. Pea cultivation technology // Grain crops, 2000; 4. Kuznetsova G.S. Plant growing // Yekaterinburg: UrGSHA, 2004. |
vse-v-ogorod.ru
Perhaps, everyone at least once heard the expression “under King Peas” ... Of course, perhaps, uttering these words, people involuntarily recalled a certain king who ruled for more than one century and bore the nickname “Peas”, but also the well-known grain crop peas, which was in honor even in pagan Russia and ancient China, deserves, if not the royal title, then at least respect.
Peas (lat. Pisum) is an annual self-pollinating herbaceous plant of the legume family. The homeland of peas is Southwest Asia, where it was cultivated in the Stone Age. The pea curls, its grassy stems reach a length of up to 250 cm. The petioles of the leaves end in tendrils, which, clinging to a support, hold the plant upright.
Peas, as well as other leguminous plants, are an excellent green manure; it enriches the soil with nitrogen. Beneficial microorganisms develop in the root zone of the plant and on the roots themselves, which are able to assimilate atmospheric nitrogen, accumulating it in the soil.
The best predecessors for peas are cucumbers, pumpkins, potatoes and cabbage, and peas themselves are the best predecessors for all crops without exception. I will tell you a little secret - potash and phosphate fertilizers should be applied under the predecessors of peas, then its fruits will have a more delicate taste. According to my personal observations, on a site that has just been fertilized, growing peas is not practical - the peas will be very leafy, but there will be very few pods. In the spring, just before sowing peas, I additionally add only compost - right into the furrow, 15 g of urea and half a teaspoon of boric acid per 1 sq. m.
Since peas are a fairly cold-resistant crop (seedlings can withstand frosts down to -6 ° C), I start sowing it early enough, as soon as the soil dries up, but not earlier than April 20. Summer sowing of peas can be done until July 10, although this only applies to early ripening varieties.
Peas are very fond of fertile light soils and absolutely cannot stand poor soils and an excess of readily available nitrogen, keep this in mind when planting it. Peas are quite picky about lighting, so try to plant them in sunny areas, protected from the winds as much as possible.
Planting peas repeatedly, I gathered one of the best crops when I planted the plant in the near-trunk circles of young apple trees. Their crowns were still quite small, so there was quite enough light for peas, and such plantings also benefited apple trees - they retained moisture in the soil, enriching it with nitrogen.
You can sow peas not only with germinated, but also with dry seeds, for example, I warm up pea seeds before sowing by dipping for 5 minutes in a hot - about 40 ° C - solution of boric acid (2 g of acid per 10 l of water). Thanks to such a simple method of pre-sowing treatment, the probability of plants being damaged by the larva of the nodule weevil, one of the dangerous enemies of peas, is significantly reduced.
The seeding rate is about 80-130 seeds per 1 sq. m. It is necessary to close up pea seeds to a depth of about 3-5 cm, depending on the soil. For example, on clay soil, the seeds need to be planted deeper, and on sandy, light soils, the seeds are planted, on the contrary, smaller.
I take a flat chopper and make a furrow about 20-25 cm wide with a distance between such furrow rows of 50-60 cm or equal to the height of the plants (see the package). I fill the furrow with compost and, having mixed it with the ground, I level it, bringing it to a depth of about five centimeters. Further, at a distance of about 5 cm from each other, I distribute peas in a ridge and, sprinkling them with earth, thoroughly compact the earth from above. Seedlings of peas, as a rule, appear within 6-15 days after sowing.
Caring for peas will not give you much trouble, since it only consists in sheltering seedlings, weeding, watering and, of course, timely harvesting.
As soon as the first shoots of peas appear, they must be protected from birds, for this I cover the shoots with an ordinary fishing net.
Repeatedly planting peas, I noticed that the plant simply does not tolerate heat, so in dry weather it must be watered very plentifully - 9-10 liters of water per 1 square meter. m. It is desirable to combine watering with top dressing, for which we dilute 1 tablespoon of nitroammophoska in 10 liters of water. Immediately after watering, the soil around the peas should be mulched. In general, the soil around pea plants, especially in the initial period of its growth, needs to be loosened, and the plants themselves should be hilled.
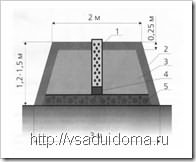
Peas also need to build supports - immediately after planting the seeds, I drive in pegs directly near the plant, at a distance of a meter from each other. I attach a special metal mesh with large cells to the pegs - about 10x10 cm, in the future it will not allow the peas to break and fall.
Peas bloom 28-60 days after sowing. About a month after the mass flowering, I start harvesting, which, by the way, perfectly stimulates the growth of peas. Since peas belong to multi-harvest crops, the period of its fruiting is quite extended and lasts about 33-42 days. I try to collect shoulder blades of peas quite often - literally in a day or two. I will tell you frankly - for the last season, observing the correct agricultural practices for growing plants, I collected about 4 kg of peas per 1 sq. m, which made me very happy.
If your goal is to get not green, but mature bean grains, peas should be left to ripen on a bush until the lower pods of the plant are fully ripe. After that, we cut the plant at the root, tie it into small bundles and hang it for final ripening for one and a half to two weeks in a ventilated room. Remember, pea seeds remain viable for 2 years.
After the peas are harvested, I cut off the tops and put them in a compost heap, and simply chop the roots and dig them right into the ground - the fertilizer is excellent. By the way, such a fertilizer can not only perfectly replace manure, but also significantly increase soil fertility, while improving its structure.
Peas are an incredibly useful crop in crop rotation, but despite the fact that it perfectly enriches and improves the soil, it can be planted in one place no earlier than after 5 years. Otherwise, there is a risk of exposing the plant to various diseases.
Perhaps the most malicious enemy of peas is the leafworm or pea codling moth, whose caterpillars hibernate in the soil. The emergence of moth butterflies from the cocoon, as a rule, just coincides with the moment the peas begin to bloom. Each moth butterfly lays about two hundred eggs on leaves, beans, stems and flowers of peas. About a week later, small caterpillars appear from these testicles, which, getting inside the beans, eat peas, and gardeners are left without a crop.
There are many methods of dealing with pea codling moth, but I use only a couple, and I will share them with you. So, to combat the pea codling moth, I periodically spray the plants with an infusion of tomato tops and garlic. To prepare the first, I take about three kilograms of tops per 10 liters of water, and for the preparation of the second, I take 20 g of garlic, passed through a garlic press, and, pouring 10 liters of water, I insist for a day. I filter the infusion and spray it with pea plants. It helps very well, by the way, both tomato and garlic infusion and from such a pest as pea aphids.
A fairly common disease of peas is powdery mildew, I prefer to deal with it using an infusion of field sow thistle - 300 g of leaves of the plant insist overnight in a bucket of water. Spraying peas with this infusion twice, with an interval of about 7-8 days.
In nature, there are several varieties of peas: sugar, which not only have edible fruits, but can also be eaten along with the wings - my favorite, as well as shelling, these have inedible wings, but their fruits are also characterized by excellent taste qualities.
Peas Adagumsky
Adagum is one of my favorite mid-season varieties, the fruits of which are distinguished by high palatability and are excellent for canning. The plant is up to 80 cm long. Mature pea seeds are green-yellow in color.
Peas Ambrosia
Ambrosia is one of the best early-ripening sugar varieties of peas, the period from germination to its technical ripeness is about fifty days. The height of the stems of a plant that needs to be supported is about 50-70 cm.
Peas Vera
Vera is an early variety, distinguished by excellent taste, suitable both for fresh use and for processing. The growing season is about 47-60 days. The stem is up to 65 cm high, the pod is straight or slightly curved, with a strong parchment layer. This variety is susceptible to ascochitosis and can be slightly damaged by the pea codling moth. The variety is valuable for its stable yield and resistance to lodging.
Pea Sphere
Sphere is also one of the most popular early varieties of shelling peas. The length of a simple stem is up to 80 cm. Pea seeds of the Sphere variety are round, semi-brained, yellow-green in color. The variety is moderately resistant to root rot.
Peas Era
Era is a mid-late shelling pea variety with a simple, slightly branched stem. The variety is moderately resistant to downy mildew and lodging.
The spread of a culture is determined by how it useful properties, and a simple technology for growing peas. This cold-resistant plant is not demanding on the composition and fertility of the soil, and the presence of nodule bacteria on the roots, which enrich the earth with nitrogen, makes it a good predecessor for all vegetable crops. However, in order to obtain high yields, it is necessary to take into account some features of pea farming.
The place for planting should be sunny, with a lack of lighting, the yield decreases, the taste of the blades and seeds deteriorates.
The plant develops well on any soil, except for acidic ones, which must first be limed.
Pea seeds are planted as early as possible, in April, when there is still enough moisture in the ground necessary for the germination of peas. In this case, the air temperature is not of great importance, since the grains germinate at +1 - +2°C, the seedlings endure a temperature drop to -6°C.
Seeds are planted in rows, every 5-6 cm, with row spacing of 15-20 cm. Seeding depth is 3-4 cm, with a shallower planting of grain, birds peck out.
Plants need to be watered regularly, because the lack of moisture causes the flowers and ovaries to fall off. However, groundwater stagnation is harmful, as it causes rotting of the root system, which lies to a depth of 1.5 m.
With proper pre-sowing soil preparation, top dressing is not required. The plant needs additional nutrition only at the beginning, before flowering, after which nodule bacteria on the roots begin to assimilate atmospheric nitrogen. Peas develop best when filling the soil with organic matter for the previous crop. Direct application of manure causes an increase in green mass to the detriment of flowering and fruit set. It is permissible to introduce rotted organic matter only during autumn digging. In spring, if necessary, seedlings can be fed with mineral nitrogen fertilizers.
Peas are harvested for grain once when 70% of the crop is ripe, for fresh use or canning - many times, after a few days, blades of sugar varieties - after 1-2 days.
One of the common and favorite crops grown in summer cottages is peas. Planting and caring for it in this case is in many ways similar to those on an industrial scale, but it also has a number of differences.
When growing peas in the country, the lack of soil moisture during the period of germination can be compensated for by abundant watering, therefore, in order to extend the time of using the fresh vegetable, it is planted at several times, with an interval of 10 days. The last date for planting peas is the end of May, as the plant bears fruit better with a long daylight hours. For better germination of seeds, they are pre-soaked for 12-18 hours, regularly changing the water every 3-4 hours, and a small amount is germinated in a damp cloth.
The scale of cultivation in the country or personal plot small, so you can use tall, and therefore more productive varieties. They require support in the form of stamens, nets, etc., which cannot be provided in the field during the industrial cultivation of peas.
Another interesting agrotechnical technique, typical for small volumes of vegetable production, is joint planting of crops. This allows not only to get a larger crop from a smaller area, but, with the right selection of plants - neighbors, to improve the conditions for each of them. It has been noticed that peas go well with carrots, corn, while, as an early ripening crop, it does not compete with them for nutrients in the initial period of growth, since at this time compacted plants develop slowly, and later, on the contrary, enriches the soil with nitrogen. As for planting potatoes with peas, different authors have different opinions on this matter. Those who consider such a neighborhood appropriate, recommend planting it simultaneously with potatoes right in the hole.
Otherwise, caring for peas in a summer cottage is the same as when growing in the fields.
For growing peas at home, sugar varieties are used, in which green shoulder blades are eaten. Plants are placed on balconies and loggias. Peas are planted to a depth of 2-3 cm in boxes or pots filled with moist loose soil, with a distance of 5-6 cm. In case of insufficient development, seedlings are fed with a weak solution of nitrogen fertilizers. Upon reaching 10-15 cm in height, the plants are provided with support, for example, a large-mesh net is hung, and then individual specimens are regularly sent along the trellis so that they do not lie down and do not obscure each other. The rest of the care consists in timely watering and loosening. Before flowering, it is watered moderately, since with an excess of water the plants pamper themselves, and after the appearance of flowers and the formation of pods, it is more plentiful. Peas do not need top dressing, for its development there is enough nitrogen absorbed from the air by nodule bacteria located on the roots.
The plant requires good light, so when grown in a room in winter, it is used not for pods and seeds, but for juicy greens eaten as a salad. Pea seeds germinate faster and produce more green mass than traditional onions and lettuce, and in terms of the content of nutrients they can compete with any vegetable crop: 100 g of young shoots contains a daily dose of vitamin C. For growing on greens, low-growing varieties with thick fleshy leaves are recommended, which are planted in small portions at several times. The most delicious and juicy greens in plants in the phase of 3-5 leaves. Further, after the stem becomes coarse, it is cut off, after which the growing shoots can also be used for food.
Peas are sown in early spring, and the soil is prepared for it in the fall. The earth is dug up to a depth of 20-30 cm, applied per 1 sq. m 4-6 kg of compost or humus, 15-20 g of potassium salt, 20-40 g of superphosphate. In the spring, during loosening, ash is added.
A particularly large yield of peas can be obtained if the soil has been well fertilized for the previous crop. Only rotted manure can be applied under peas, fresh manure cannot be used - it causes excessive growth of green mass to the detriment of the formation of flowers and fruits.
The best predecessors for peas are early potatoes, cabbage, tomatoes, pumpkin. The pea itself, like other legumes, is the best predecessor for all crops. You can return peas to their old place no earlier than after four years.
Almost any soil is suitable for peas, its mechanical composition is not so important, it can be clay, loamy, and sandy. Acidic soils should be preliminarily limed (300-400 g of lime per 1 sq. M).
Under the peas, it is necessary to allocate a sunny place, avoiding the close occurrence of groundwater, since the roots of the plant penetrate deeply into the soil - a meter or more.
Peas are grown in a seedless way. The seeds are pre-soaked - they are poured with water at room temperature so that it covers them completely, and kept for 12-18 hours, changing every 3-4 hours. You can treat peas with growth regulators (within 2-3 hours) or warm them up for 5 minutes in hot water, dissolving micronutrient fertilizers in it. If there are few seeds, they are kept in a damp cloth until they begin to germinate. Prepared seeds are sown in moist soil.
Sowing starts very early, from the end of April. As a cold-resistant crop, peas germinate already at 4-7 ° C, seedlings can withstand frosts down to -6 ° C, but still, with early sowing, it is better to close the bed with a film. Peas are sown in several terms with a shift of 10 days. The last time it is better to do this at the end of May, since the plant can successfully bloom and bear fruit only during the period of long daylight hours.
Usually, peas are sown in rows with a distance between them of 15-20 cm, between plants in a row - 5-6 cm. Grooves are made and peas are laid out in them. The soil is leveled and lightly compacted. Planting depth - 3-4 cm. If the seeds are planted too shallow, birds can peck out, so in order to avoid misunderstandings, it is better to cover the crops with non-woven material. After a week and a half, shoots appear.
If wide (40-45 cm) aisles are made on the beds where peas are planted, then lettuce or radish can be sown in them. Peas are also grown in the trunk circles of apple trees, if there is enough light. To do this, it is necessary to add fertile soil to a height of 10-12 cm.
vegetable peas belongs to the legume family (Fabaceae). His appearance is well known to everyone: a tetrahedral stem up to 2.5 m high, sometimes branches.
The leaves are paired, usually ending in antennae. Flowers of various colors, up to seven pieces. The fruits are beans, and the seeds are peas, smooth or wrinkled (the inscription on the jars "green peas of brain varieties" is about the latter).
Vegetable peas are divided into two groups: sugar and shelling. Sugar beans, or shoulder blades, are tender and sweet. The wings can be eaten whole - they remain juicy until the end of wax ripeness.
In varieties of shelling peas, the inside of the bean flaps is covered with an inedible parchment layer. Use only immature seeds - "green peas".
Varieties of vegetable peas are divided into peeling and sugar. Shelling varieties have a coarse parchment layer on the inside of the bean, and only grains are used for food. Sugar varieties have juicy fleshy flaps, without a parchment layer, they are used on a shoulder blade - as a whole or in the form of green peas. Within these groups there are varieties with rounded, smooth and wrinkled grains (brain peas).
Peas are the most cold-resistant vegetable plant (tolerates frosts down to -4 C), especially varieties with rounded, smooth seeds. Such seeds germinate at 1-2 C, brain seeds at 4-8 C. The optimum temperature for seed germination and subsequent growth of pea plants is 16-20 C.
Pea is a crop that is demanding on soil moisture, especially during the period of seed germination and in the first growing season, it tolerates excess soil moisture well, but does not withstand high standing groundwater. The optimum soil moisture for peas is 75-80% of the FWC (Total Field Capacity). However, peas are resistant to short-term droughts. Thanks to a powerfully developed root system, plants can provide themselves with moisture, extracting it from deeper layers of the soil.
Vegetable peas are grown after any predecessors, but the best for it are those under which manure was applied - root crops, cucumbers, tomatoes, cabbage, potatoes. You can return vegetable peas to the same site no earlier than after 4 years. The best soils for peas are well-cultivated and fertilized light loamy and sandy loamy soils. You can also grow peas on heavy and drained soils, but plants on such soils are more oppressed and do not provide the maximum possible yields.
Depleted acidic, alkaline soils with a high level of groundwater are unsuitable. The main tillage for peas consists in the autumn destruction of plant residues of the predecessor and weeds and subsequent deep autumn plowing or digging to a depth of at least 22-25 cm.
Early in the spring, the plowing is leveled.
Seeding (planting) rate - 16-24 g/m2 (depending on variety and size of seeds).
Peas are sown early, but in mature soil, first early-ripening varieties, and then medium and late. This work must be completed no later than April 1-5. Later dates sharply reduce the yield of peas. Sowing can also be carried out during the February-March thaws.
Peas take relatively few nutrients out of the soil. In addition, the pea root system can assimilate nutrients from mineral compounds that are hard to reach for other plants, fix nitrogen from the air with the help of nodule bacteria.
Therefore, on fertile soils, the effectiveness of fertilizers applied under peas is low. On such soils, fertilizers are best applied under the previous crop. On infertile soils, the effectiveness of both organic and mineral fertilizers increases. In addition, the application of mineral fertilizers increases the sugar content, inhibits the accumulation of starch in green peas, which improves its quality.
The main task of caring for vegetable pea plants is to keep the soil clean from weeds, provide plants with moisture and control pests and diseases. Creation of optimal growing conditions - from the beginning of the flowering of vegetable peas to its end, when intensive
formation of ovules and seeds. This creates good conditions for a high yield. During the period of plant growth, as the soil dries out, watering is carried out. When growing peas "on the shoulder" or green peas, it is watered 2-3 times, and for mature grain during the growing season it is watered 3-4 times. Irrigation rate is 3.5-4.5 liters per 1 m2. Sugar varieties include:
Zhegolova-112- a mid-late-ripening variety, with a tendency to some reduction in the growing season in conditions of rising temperatures. From germination to flowering 35-45 days, to technical maturity - 50-60 and to ripening - 90-110 days. The ripening of the beans on the plant is quite amicable. The yield of beans is up to 14.5 q/ha. The taste of unripe fruits is good. It is unstable to lodging, in wet years it is affected by pale-spotted and dark-spotted ascochitosis. Seeds are rounded-angular, somewhat flattened, light bluish-green, the hilum is light.
Inexhaustible-195- medium-early ripe variety, from germination to flowering 35-38 days, to technical maturity 46-60, to ripening 70-90 days. The ripening of the beans on the plant is quite amicable. The yield of beans is 65 - 80 kg / ha (65 - 80 kg per hundred square meters). The taste of unripe beans is good. Seeds are angularly compressed, yellow-green (two-color), fading to yellow at high temperatures, the hilum is light. Adagum- mid-season variety, from germination to flowering 50-56 days, to technical maturity 68-73, to ripening 77-80 days. Productivity is high, beans in technical ripeness 150-160 kg/ha, peas - 72-96 kg/ha. Peas in technical ripeness are dark green, even in color and size. The palatability is high, it is slightly affected by powdery mildew and ascochitosis. The seeds are square-squeezed, yellow-green (two-color), yellow when overripe, unripe - gray-green, the scar is light.
Aalpha (Gloriosa improved)- an early ripe variety, from germination to flowering 28 - 35 days, to technical maturity 45 - 53, to ripening 63-71 days. The yield of green peas is high. The yield of beans in the phase of technical ripeness is 85-108 and peas 48 - 90 q/ha. Ripening is friendly. Peas in the phase of technical ripeness are dark green, even in color and size. Taste is high. Weakly affected by ascochitosis and fusarium. Seeds are square-squeezed yellow-green (two-color), the hilum is light.
Jubilee-1512- mid-late-ripening variety, from germination to flowering 51-62 days, to technical maturity 69-79, to full maturity 74-89 days.
The yield of beans in the phase of technical ripeness is 120-150 and green peas - 55-71 c/ha. Peas in technical ripeness are dark green. Taste qualities are good. Weakly affected by ascochitosis. The seeds are square-compressed, mostly light gray-green, with some overripe - yellow-green (two-color), the scar is light.
Kubanets-1126- the variety is early ripe, from germination to flowering 37 - 45 days, to technical maturity - 55-69, to ripening - 71 - 80 days. The yield of beans in the phase of technical ripeness is 138-145, green peas - 55-58 c/ha. Peas in technical ripeness are dark green, good taste. Moderately affected by ascochitosis and moderately affected by aphids and codling moth. Seeds are angular and square-compressed, yellow-green (two-color), the scar is light.
Vegetable-76- mid-early ripe variety, from germination to flowering 35-42 days, to technical maturity - 58-69, to ripening - 68-77 days.
The yield of beans in the phase of technical ripeness is 120-190, green peas - 52 - 95 kg / ha. Peas in technical ripeness are light green and green. Taste is good and excellent. Not resistant to ascochitosis and pea codling moth. Seeds are square-compressed, yellow-green (two-color), the hilum is light. The bean is straight or slightly curved, with a pointed apex, dark green in the phase of technical ripeness, 8-10 cm long, 1.3-1.4 cm wide, 8-10 seeds per bean.
Late brain improved- late-ripening variety, from germination to flowering 54-55 days, to technical maturity - 76-84, to ripening - 90-106 days. The yield of beans in the phase of technical ripeness is 82-90, green peas - 35 - 52 kg / ha. Peas in technical ripeness are dark green, even in size and color. Taste qualities are good. It is affected by ascochitosis. Codling moth is affected in the years of mass development of the pest. The seeds are angularly compressed, light bluish-green, fading to greenish-yellow in excess, the scar is light. There are 7-9 seeds in a bean.
Excellent-240- mid-season variety, from germination to flowering 41-51 days, to technical maturity 64-70, to ripening 69-80 days. The yield of beans in the phase of technical ripeness is 120-170 and green peas - 53-78 q/ha. Differs in amicable formation of a crop. Peas in technical ripeness are intense green, even in size and shape.
Taste qualities are good. It is strongly affected by ascochitosis and powdery mildew. Seeds are angular-square, yellow-green (two-color), sometimes fading to greenish-yellow, the hilum is light. The flower is white, of medium size, mostly two per peduncle. The bean is curved, with a pointed top, dark green in the phase of technical ripeness, 8 - 9 cm long, 1.2 - 1.4 cm wide, seeds in a bean 6 - 9 pieces.
Early canning-20/21- an early ripe variety, from germination to flowering 45-54 days, to technical maturity 58-67, to ripening - 65-70 days. The yield of beans in the phase of technical ripeness is 85-112 and green peas - 42 - 61 kg / ha.
The ripening of the beans is friendly. Peas in technical ripeness are dark green. Taste qualities are good. It is prone to be affected by ascochitosis, the codling moth is affected moderately, in some years above average. Seeds are angular-square, yellow-green (two-color), fading to yellow, the hilum is light. The flower is white, of medium size, mostly one per peduncle. The bean is straight or slightly curved, with a blunt or less often almost rounded top. The parchment layer is somewhat less developed than in other peeling varieties, in the phase of technical ripeness it is dark green, 5.5 - 8.0 cm long, 1.2 - 1.4 cm wide, more than 7 - 9 seeds.
Early Gribovsky II- a variety of early ripening. The stem is low (35 - 40 cm), resistant to lodging, internodes are short.
The flowers are white, the first inflorescence is laid on the 9-10th node. The beans are large, pointed, in the phase of technical ripeness they are dark green in color. Seeds are greenish-yellow, medium or above average size. Weight of 1000 seeds 220-250 g.
Vega- a variety of medium early ripening. The stem is simple, indeterminate type of growth, with short internodes, the number of nodes up to the first pod is 12-13. D
stem length up to 65 cm. White flower. Bean shelling, straight, with a pointed top, up to 8.4 cm long, with 7 - 8 seeds. In the phase of technical ripeness it has a dark green color. Seeds are cerebral, with a wrinkled surface, angular-square, weight of 1000 seeds is 220-247 g. Seed skin is colorless, color of cotyledons is yellow. Productivity under production conditions is 7 - 8 t/ha.
Fugue- a grade of average term of maturing - from shoots before harvesting in a phase of technical ripeness of 65 days. The stem is simple, 60 cm long, the internodes are short, the number of nodes up to the first pod is 14-16. The flower is white, medium size. Bean shelling, straight, 10 × 1.5 cm, with a pointed top, dark green in the phase of technical ripeness, 9-10 seeds. Brain seeds with a wrinkled surface, angular-square, colorless skin, green cotyledons, weight of 1000 seeds up to 250 g. Yield 15.3 t/ha. Resistant to Fusarium wilt.
Peas are a long day plant, i.e. For flowering and fruiting, daylight hours are needed, lasting more than 13 hours. With a short daylight hours (less than 12 hours), seeds are not formed. Peas are an undemanding plant to grow. ( discussion of the features of growing vegetables)
vyrastisad.ru

When choosing varieties for sowing, pay attention to the best properties of this wonderful plant.
Peas come first among all vegetables in terms of nutritional value and energy boost that it gives. In terms of calories, it surpasses some varieties of beef. No wonder pea jelly is called satiety. Nutritionists believe that an adult needs to eat at least 4 kg of green peas per year.
If you grow peas on the same acres all season, the soil will accumulate up to 10 kg of nitrogen, which corresponds to the introduction of 1-1.5 tons of manure. In addition, its root system converts mineral compounds that are difficult for plants to absorb into available ones and extracts nutrients from deep soil layers. So
Peas can replace top dressing, worms, and a cultivator.
In early spring, several varieties can be sown at the same time and then eat fresh green peas for 2 months. If you correctly distribute the timing of sowing different varieties throughout the season, you can feast on peas from the garden for 90-100 days.
Such a green pipeline will provide:
- Zamira, Misty, Hezbana, Corwin(38-40 days after germination);
- Asana, Abador, Vinko (41-46);
- Sherwood, Ashton (47-55);
- Nicholas, Twin, Matron (56-61);
- Pecan (62-68).
All these are peeling pea varieties.
In sugar peas, which does not form fibers, you can eat the whole bean, remain unsurpassed Zhegalova 112(mid-season), Inexhaustible 195(late maturing).
From "bean relatives" - clover, alfalfa, beans - growing nearby peas begin to get sick and suffer from pests. But he feels good in the aisles of the garden, where after harvesting the entire aerial part of the plant should be embedded in the ground. The neighborhood of apple trees with peas mutually adds to the harvest.
When to harvest green peas. It is better to collect green peas in the early morning, as they quickly wither in the heat of the day. Green peas in beans are stored for 10-12 hours, and shelled 3-4, after which it becomes starchy and less sweet. The mesh on the beans indicates that they are overripe.
A large crop of peas is either dried or canned. Dry peas are stored for more than 10 years, retaining their healing and nutritional qualities, and canned peas are best used within a year or two.
New products are Urbana, Omega, Resal, Sweet friend, Maxdon, Legacy. These varieties are sweeter,
Varieties, and sugar peas are often smooth.
So it turns out that brain peas are sweeter than sugar peas.